Weather intelligence for the future: Crafting a strategic enterprise approach to changing environmental conditions
Continue readingNew Modeling System GRAF Offers More Timely and Precise Local Forecasts, Democratizing Weather Around the Globe
ARMONK, N.Y. and ATLANTA, Nov. 14, 2019 — IBM (NYSE: IBM) and its subsidiary The Weather Company today announced the global rollout of a new supercomputer-driven weather forecasting system that will provide fresher, higher quality forecasts in parts of the world that have never before had access to state-of-the-art weather data.
Experience the interactive Multichannel News Release here: https://www.multivu.com/players/English/8247557-ibm-the-weather-company-graf-forecasting-system/
Known as GRAF, the Global High-Resolution Atmospheric Forecasting System can predict conditions up to 12 hours in advance with detail and frequency previously unavailable at this global scale.
GRAF will provide much finer-grained predictions of the atmosphere and update its forecasts six to 12 times more frequently than conventional global modeling systems. Current global weather models cover 10-15 square kilometers (6.2-9.3 miles) and are updated every 6-12 hours. By contrast, GRAF forecasts down to 3 kilometers (1.9 miles) and is updated hourly.
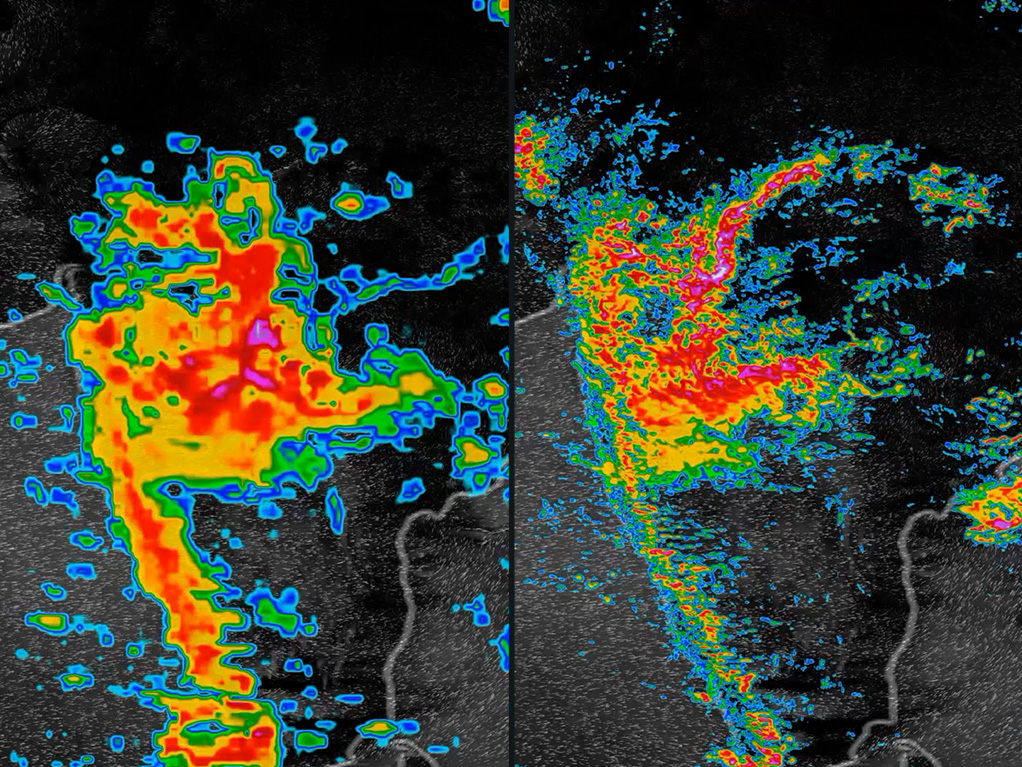
An August 2018 monsoon in India, shown at left by the best current weather model that operates at 13-kilometer resolution. At right, The Weather Company’s new Global High-Resolution Atmospheric Forecasting System (GRAF) operates at 3-km resolution and updates 6 to 12 times more often.
This level of forecasting precision has been available in the U.S., Japan and a handful of Western European countries. But the launch of GRAF marks the first time such enhanced forecasts cover more of the globe, including Asia, Africa and South America, areas among the most vulnerable to the increasingly intense extreme weather resulting from climate change. GRAF is the world’s first operational high-resolution, hourly-updating model that covers the entire globe.
“We view the launch of GRAF as a true inflection point in forecasting science, where technology helps democratize weather data for the good of society,” said Cameron Clayton, head of The Weather Company and general manager of IBM’s Watson Media and Weather. “The enhanced forecasts could be revolutionary for some areas of the world, such as for a rural farmer in India or Kenya. If you’ve never before had access to high-resolution weather data but could now anticipate thunderstorms before they approach your fields, you can better plan for planting or harvesting.”
Collaboration helps create improved global modeling of the atmosphere
To build the new modeling system, The Weather Company collaborated with the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) to create GRAF based on NCAR’s next-generation open-source global model, the Model for Prediction Across Scales, which uses state-of-the-art science to forecast the atmosphere down to thunderstorm level on a global scale.
As the world contends with climate change and more intense severe weather events globally, timely and accurate weather information is increasingly important. To help meet future challenges, strong public-private partnerships across governments, businesses and research institutions and open-source collaboration can continue to help advance science and technology at a more effective pace.
Advanced supercomputing allows for higher workloads
Forecasting weather is a complicated mathematical problem, requiring high-performance computing to solve complex equations. Traditionally, most weather models use high-performance computers built only with CPUs (central processing units). To handle its increased resolution and update frequency, the new GRAF system runs on an IBM POWER9-based supercomputer optimized for both CPUs and GPUs (graphics processing units), powerful compute engines widely deployed for demanding high-performance computing and AI applications.
IBM is applying the same technology behind some of the world’s most powerful supercomputers to weather forecasting. The Weather Company and IBM, together with NCAR, the University of Wyoming’s Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and others applied OpenACC directives to MPAS to take advantage of NVIDIA V100 Tensor Core GPUs on an IBM Power Systems AC922 server.
This is the world’s first global weather model to run operationally on a GPU-based high-performance computing architecture.
A better picture of weather globally
Other models may be high-resolution or update often, but the resulting forecasts only cover one country or region of the world. This is the first time a full global model exists to provide forecasts for the day ahead at this scale, resolution and frequency.
A clearer sense of exactly when and where impactful weather will surface can help when planning and preparing for weather. Whether it’s an airline, a utility company, a daily commuter, a retailer, a government decision-maker, or a farmer, GRAF predictions can help people, governments and businesses around the world make more informed weather-related decisions.
Leveraging GRAF to help in decision-making also requires technologies such as AI, cloud and analytics. Combining these additional technologies enables predictions from GRAF to help power IBM weather offerings for businesses and to drive weather content within apps and websites by The Weather Channel (weather.com) and Weather Underground (wunderground.com).
SOURCE IBM
